In this post, we will see how to connect Python to SQL Server.
First of all, we create a database called DBTestPython and then, we run some sql scripts in order to create two tables and feeding them with some test data:
TABTYPE:
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[TabType](
[TypeID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[TypeDescription] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_TabType] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[TypeID] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
TABUSER:
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[TabUser](
[UserId] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[UserName] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL,
[UserTypeId] [int] NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_TabUser] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[UserId] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[TabUser] WITH CHECK ADD CONSTRAINT [FK_TabUser_TabType] FOREIGN KEY([UserTypeId])
REFERENCES [dbo].[TabType] ([TypeID])
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[TabUser] CHECK CONSTRAINT [FK_TabUser_TabType]
GO
FEED DATA:
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[TabType] ON
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabType] ([TypeID], [TypeDescription]) VALUES (1, N'Admin')
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabType] ([TypeID], [TypeDescription]) VALUES (2, N'Reader')
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabType] ([TypeID], [TypeDescription]) VALUES (3, N'Contributor')
GO
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[TabType] OFF
GO
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] ON
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] ([UserId], [UserName], [UserTypeId]) VALUES (1, N'Admin1', 1)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] ([UserId], [UserName], [UserTypeId]) VALUES (2, N'Admin3', 1)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] ([UserId], [UserName], [UserTypeId]) VALUES (3, N'UserReader1', 2)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] ([UserId], [UserName], [UserTypeId]) VALUES (4, N'UserReader4', 2)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] ([UserId], [UserName], [UserTypeId]) VALUES (5, N'UserReader5', 2)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] ([UserId], [UserName], [UserTypeId]) VALUES (6, N'UserReader6', 2)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] ([UserId], [UserName], [UserTypeId]) VALUES (7, N'UserContributor21', 3)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] ([UserId], [UserName], [UserTypeId]) VALUES (8, N'UserContributor34', 3)
GO
INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] ([UserId], [UserName], [UserTypeId]) VALUES (9, N'UserContributor36', 3)
GO
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[TabUser] OFF
Now, in order to connect Python to a Sql Server, we need to install an external package, called pyodbc, using the command
pip3 install pyodbc.
After the installation, we open Visual Studio Code and we create two files called UserItem.py and ReadData.py:
[USERITEM.PY]
class User:
def __init__(self, id, username, typeuser):
self.Id = id
self.UserName = username
self.TypeUser = typeuser
def Info(self):
print(f"ID:{self.Id} - UserName:{self.UserName} / {self.TypeUser}")
[READDATA.PY]
# import Class User
from UserItem import User
# import pyodbc
import pyodbc
# define connection string
connection = pyodbc.connect('Driver={SQL Server};'
'Server=DESKTOP-V3SF2TJ;'
'Database=DBTestPython;'
'Trusted_Connection=yes;')
def ReadData():
# define array of User
lstUser =[]
# define cursor
cursor = connection.cursor()
# define sql query
strSql = "select A.UserId, A.UserName, B.TypeDescription from TabUser A inner join TabType B on A.UserTypeId = B.TypeID"
# execute sql query
cursor.execute(strSql)
# read data
for row in cursor:
# create a list of User
objUser = User(row[0], row[1], row[2])
lstUser.append(objUser)
return lstUser
lstResult = ReadData()
for item in lstResult:
item.Info()
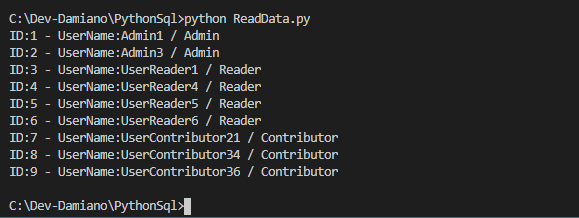
If we run the application, using the command pyhton ReadData.py, this will be the result: