In this post, we will see how to connect a Node application with the MySQL Db called “DbManagerUser”, created in the post: MySQL – How to create a DB.
First of all, we open Visual Studio Code, we open a terminal and we install the MySQL Module, using the command
npm install mysql
Then, we create an entity called “useritem” and a node.js script called “readmysql”:
[USERITEM.JS]
function UserItem(userid, username, usertype)
{
this.UserId = userid;
this.UserName = username;
this.UserType = usertype;
}
module.exports = UserItem;
[READMYSQL.JS]
// import Class "userItem"
var UserItemClass = require("./useritem")
// import MySQL
const mysql = require('mysql');
// Method definition
function ReadData(strSql, callback)
{
// Define the array result
var lstUserItem = [];
// Connection string definition
const con = mysql.createConnection({
host: '127.0.0.1',
user: 'test',
password: '$Test123',
database: 'DbManageUser'
});
// Opening the connection
con.connect((err) => {
if(err){
console.log('Error connecting to Db');
return;
}
});
// Running the query
con.query(strSql, (err,rows) => {
if(err) throw err;
rows.forEach( (row) => {
lstUserItem.push(new UserItemClass(row.UserId, row.UserName, row.UserType));
});
// define the callback
return callback(lstUserItem);
});
// Closing the connection
con.end((err) => {
if(err){
console.log('Error closing connection');
return;
}
});
}
module.exports = {
ReadData
}
Finally, we create our principal Node script called “testmysql”:
[TESTMYSQL.JS]
var objData = require('./readmysql');
var UserItemClass = require("./useritem")
var strSql = "select A.UserId, A.UserName, B.UserType from TabUser A inner join TabUserType B on A.UserType = B.IdUserType"
var lstUserItem = objData.ReadData(strSql,
// callback function
function(result){
result.forEach(element => {
console.log(element.UserId + " - " + element.UserName + " - " + element.UserType);
});
});
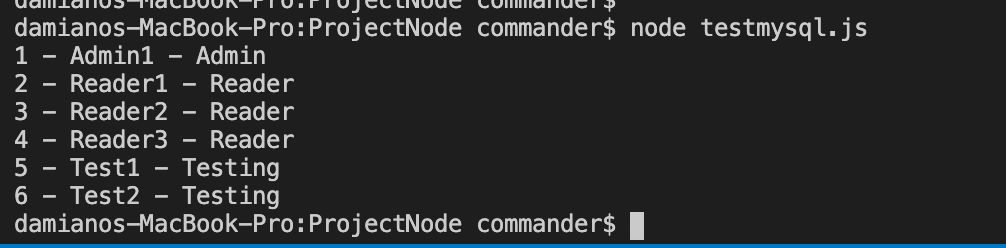
If we run the application, this will be the output: