In this post, we will see how to manage the versioning in a .net core Web API service, using three different approaches:
1) Query String-Based Versioning
2) URL-Based Versioning
3) HTTP Header-Based Versioning
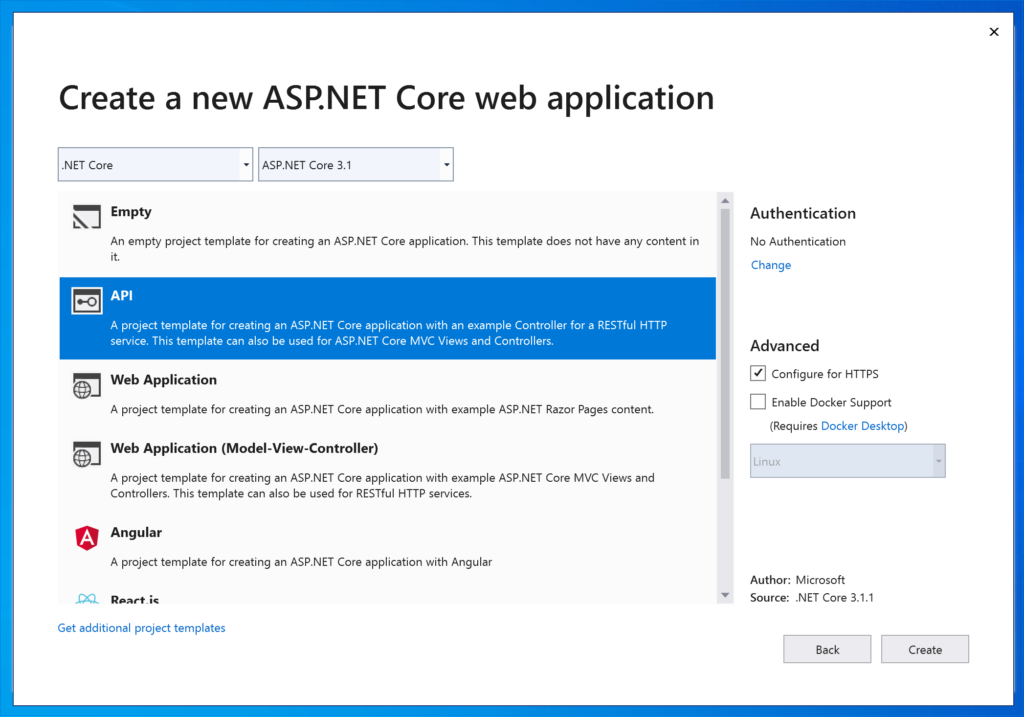
First of all, we open Visual Studio 2019 and we create a Web API project:
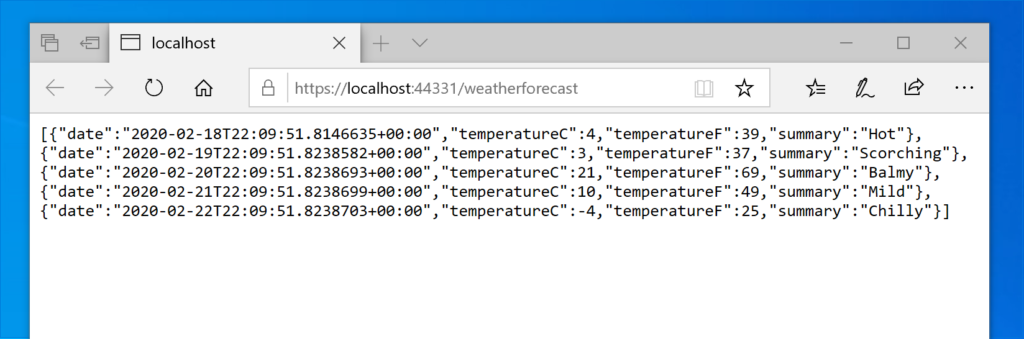
If we run the application, this will be the output:
Now, in order to manage the versioning, we have to install the library
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Versioning
and then, we have to modify the method ConfigureServices in the startup file:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services){ services.AddControllers(); services.AddApiVersioning(o => { o.AssumeDefaultVersionWhenUnspecified = true; o.DefaultApiVersion = new ApiVersion(1, 0); });} |
QUERY STRING-BASED VERSIONING:
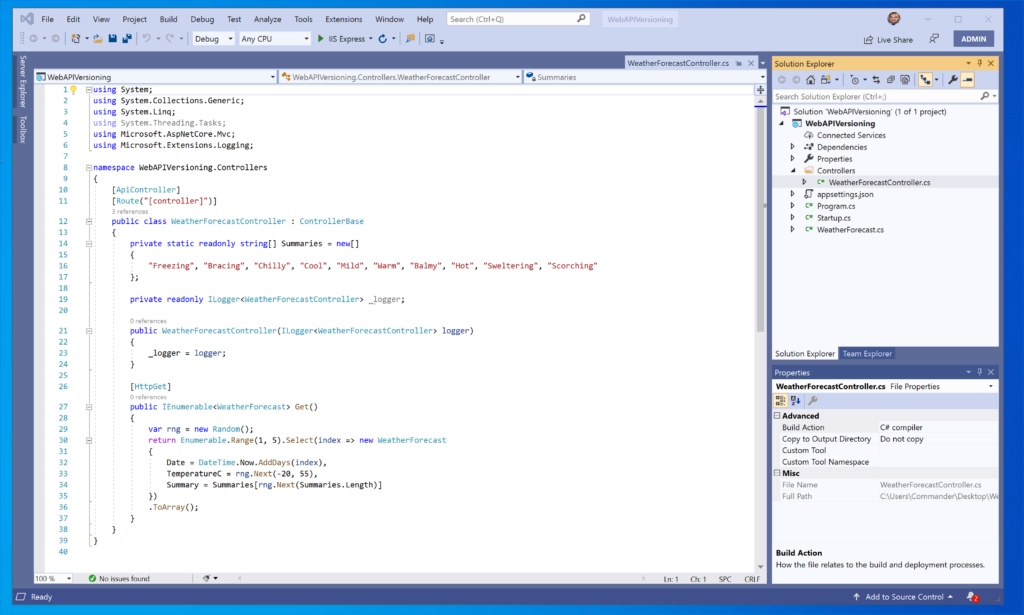
We open the file WeatherForecastController and we create two versions of the controller:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 | using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;namespace WebAPIVersioning.Controllers{ [ApiController] [ApiVersion("1.0")] [Route("api/Forecast")] public class WeatherForecastController : ControllerBase { private static readonly string[] Summaries = new[] { "Freezing", "Bracing", "Chilly", "Cool" }; private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger; public WeatherForecastController(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger) { _logger = logger; } [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get() { var rng = new Random(); return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast { Date = DateTime.Now.AddDays(index), TemperatureC = rng.Next(-20, 55), Summary = Summaries[rng.Next(Summaries.Length)] }) .ToArray(); } } [ApiController] [ApiVersion("2.0")] [Route("api/Forecast")] public class WeatherForecastControllerVersion2 : ControllerBase { private static readonly string[] Summaries = new[] { "Mild", "Warm", "Balmy", "Hot", "Sweltering", "Scorching" }; private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger; public WeatherForecastControllerVersion2(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger) { _logger = logger; } [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get() { var rng = new Random(); return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast { Date = DateTime.Now.AddDays(index), TemperatureC = rng.Next(-20, 55), Summary = Summaries[rng.Next(Summaries.Length)] }) .ToArray(); } }} |
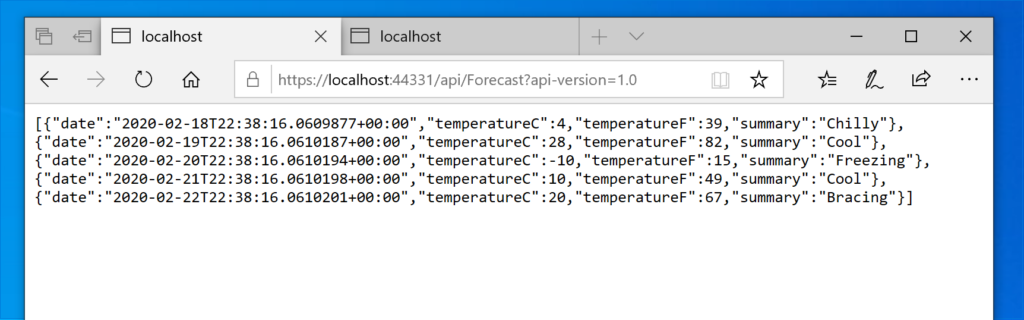
In order to call the different versions of the controller, we have to pass the version of controller in the query string:
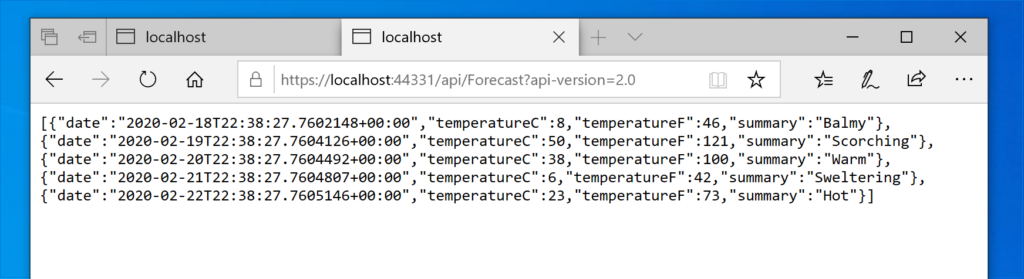
URL-BASED VERSIONING:
We open the file WeatherForecastController and we create two versions of the controller:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 | using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;namespace WebAPIVersioning.Controllers{ [ApiController] [ApiVersion("1.0")] [Route("api/v{v:apiVersion}/Forecast")] public class WeatherForecastController : ControllerBase { private static readonly string[] Summaries = new[] { "Freezing", "Bracing", "Chilly", "Cool" }; private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger; public WeatherForecastController(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger) { _logger = logger; } [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get() { var rng = new Random(); return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast { Date = DateTime.Now.AddDays(index), TemperatureC = rng.Next(-20, 55), Summary = Summaries[rng.Next(Summaries.Length)] }) .ToArray(); } } [ApiController] [ApiVersion("2.0")] [Route("api/v{v:apiVersion}/Forecast")] public class WeatherForecastControllerVersion2 : ControllerBase { private static readonly string[] Summaries = new[] { "Mild", "Warm", "Balmy", "Hot", "Sweltering", "Scorching" }; private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger; public WeatherForecastControllerVersion2(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger) { _logger = logger; } [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get() { var rng = new Random(); return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast { Date = DateTime.Now.AddDays(index), TemperatureC = rng.Next(-20, 55), Summary = Summaries[rng.Next(Summaries.Length)] }) .ToArray(); } }} |
In order to call the different versions of the controller, we have to put the version of controller in an URL path segment:
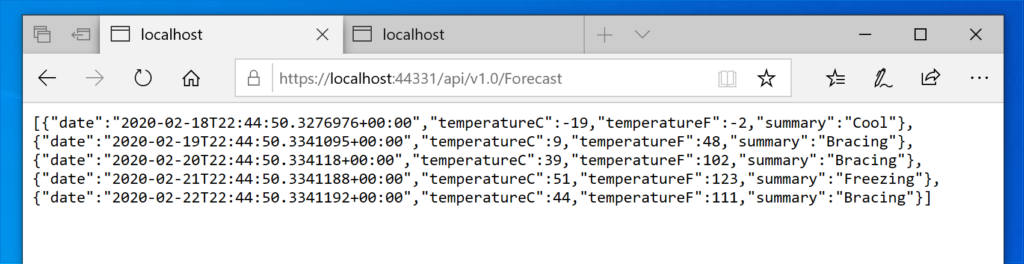
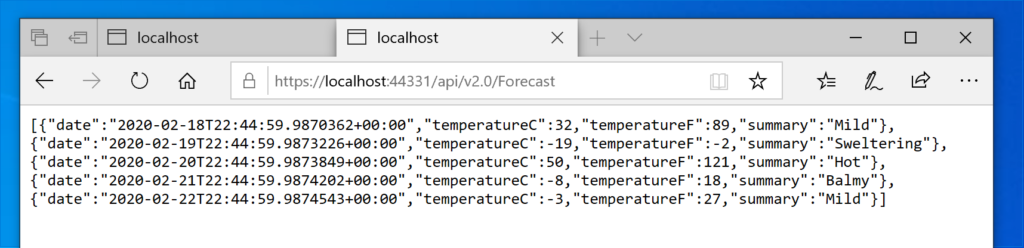
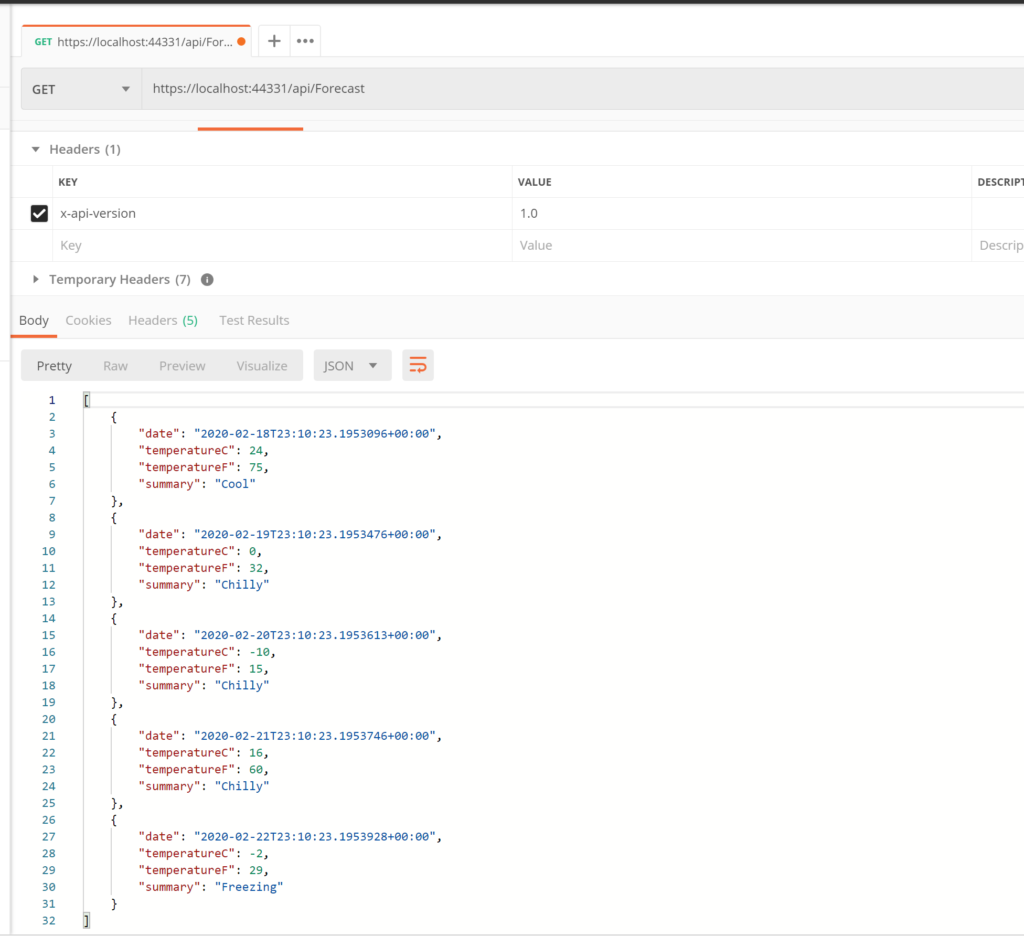
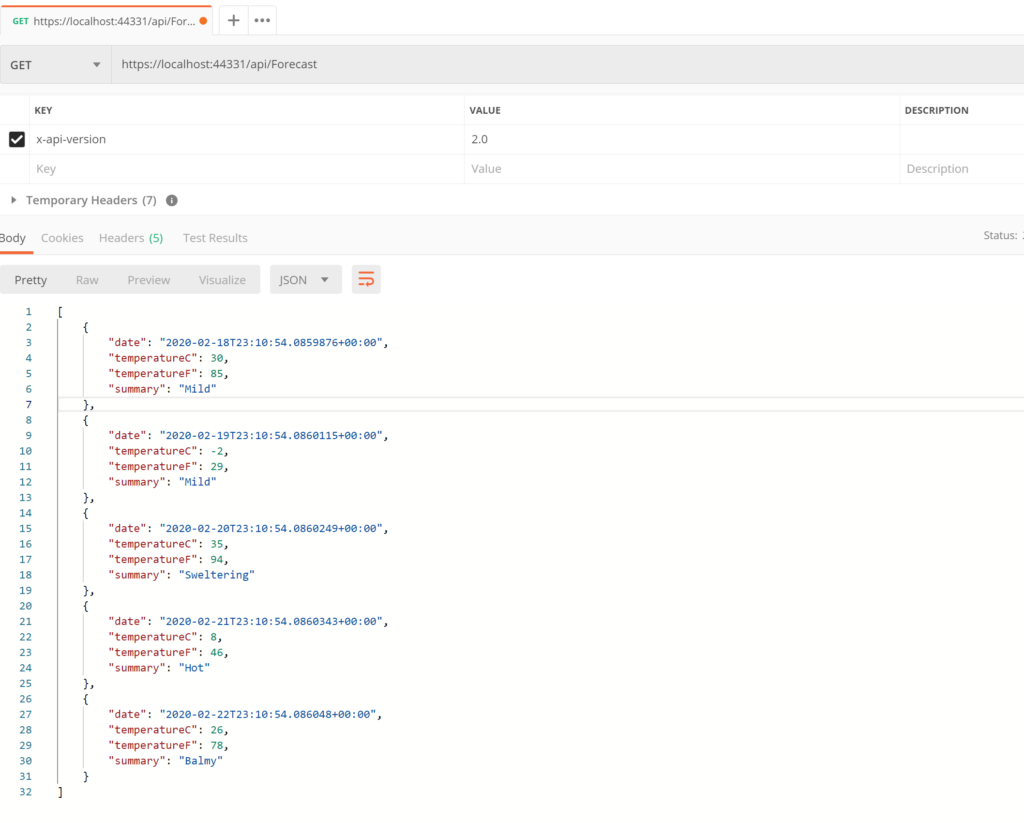
HTTP HEADER-BASED VERSIONING:
We open the file WeatherForecastController and we create two versions of the controller:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 | using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;namespace WebAPIVersioning.Controllers{ [ApiController] [ApiVersion("1.0")] [Route("api/Forecast")] public class WeatherForecastController : ControllerBase { private static readonly string[] Summaries = new[] { "Freezing", "Bracing", "Chilly", "Cool" }; private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger; public WeatherForecastController(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger) { _logger = logger; } [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get() { var rng = new Random(); return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast { Date = DateTime.Now.AddDays(index), TemperatureC = rng.Next(-20, 55), Summary = Summaries[rng.Next(Summaries.Length)] }) .ToArray(); } } [ApiController] [ApiVersion("2.0")] [Route("api/Forecast")] public class WeatherForecastControllerVersion2 : ControllerBase { private static readonly string[] Summaries = new[] { "Mild", "Warm", "Balmy", "Hot", "Sweltering", "Scorching" }; private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger; public WeatherForecastControllerVersion2(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger) { _logger = logger; } [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get() { var rng = new Random(); return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast { Date = DateTime.Now.AddDays(index), TemperatureC = rng.Next(-20, 55), Summary = Summaries[rng.Next(Summaries.Length)] }) .ToArray(); } }} |
Finally, we have to modify the method ConfigureServices, in the the startup file:
[STARTUP.CS]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services){ services.AddControllers(); services.AddApiVersioning(o => { o.AssumeDefaultVersionWhenUnspecified = true; o.DefaultApiVersion = new ApiVersion(1, 0); o.ApiVersionReader = new HeaderApiVersionReader("x-api-version"); });} |
Now, we run the application using Postman and we put in the header the controller’s version: