In this post, we will see how to create a Rest API with Node.js and Express.
First of all, what is Express?
Express is an open source web framework that helps us to make developing websites, web apps, & API’s much easier.
It supports many templating engines and it is very simple to use.
In order to install Express, we run the command npm install express:
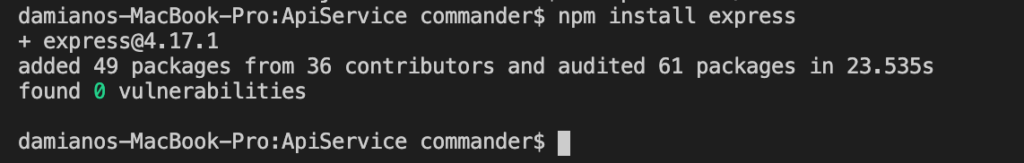
Now, we can start to create our application and first of all, we generate the package.json file with the command npm init.
[PACKAGE.JSON]
{
"name": "apiservice",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Service API",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "Damiano Abballe",
"license": "ISC"
}
Then, we define an entity called Product and a class called CoreProduct where, we will define all methods used to manage data:
[PRODUCT.JS]
// definition of a class called Product
class Product
{
constructor(id, name, price)
{
this.Id = id;
this.Name = name;
this.Price = price;
}
}
module.exports = Product;
[COREPRODUCT.JS]
// import the class Product
var productItem = require("./product")
// definition of a class called CoreProduct
class CoreProduct
{
constructor()
{
// in the constructor we feed the list of products with fake data
this.lstProducts = this.LoadAllProducts();
}
LoadAllProducts()
{
var lstProducts = [];
for(var i=1;i<10;i++)
{
lstProducts.push(new productItem(i, "Name"+i, i+10 ));
}
return lstProducts;
}
// definition of a method used into Rest API for getting the list of Products
GetAllProducts()
{
return this.lstProducts;
}
// definition of a method used into Rest API for getting the single Product by Id
GetProduct(id)
{
for (var i = 0; i < this.lstProducts.length; i++)
{
if(this.lstProducts[i].Id==Number(id))
{
return new productItem(this.lstProducts[i].Id, this.lstProducts[i].Name, this.lstProducts[i].Price);
}
}
}
}
module.exports = CoreProduct;
Finally, with the command npm install cors, we install the CORS module and then, we will create the main file called index:
[INDEX.JS]
// import express
var express = require('express');
// import cors
const cors = require('cors')
var app = express();
var CoreProduct = require("./coreproduct")
var objCoreProduct = new CoreProduct();
var product = require("./product")
// definition of Rest API's port
var port = process.env.port || 1333;
// definition of a method used to get all Products
// in a real project, we should define the list of allowed origins
app.get('/api/products', cors(), (request,response) => {
response.status(200).json(objCoreProduct.GetAllProducts());
});
// definition of a method used to get the single Product by Id
// in a real project, we should define the list of allowed origins
app.get('/api/products/:id', cors(), (request,response) => {
response.status(200).json(objCoreProduct.GetProduct(request.params.id));
});
// we run the application
app.listen(port, function () {
console.log("Server runnning on Port:- " + port + " Started at :- " + new Date());
});
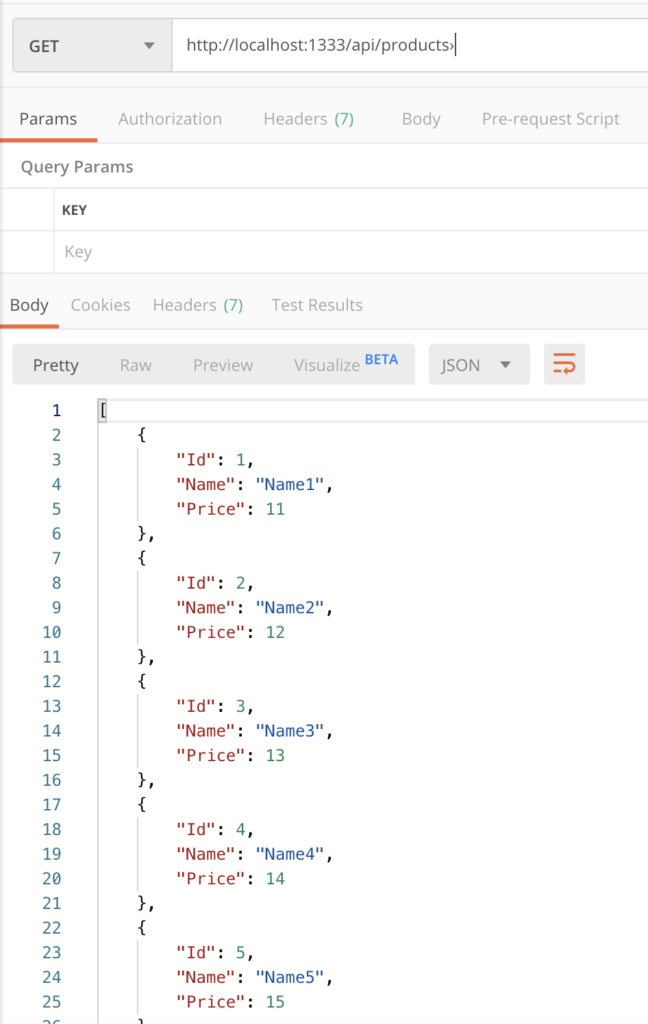
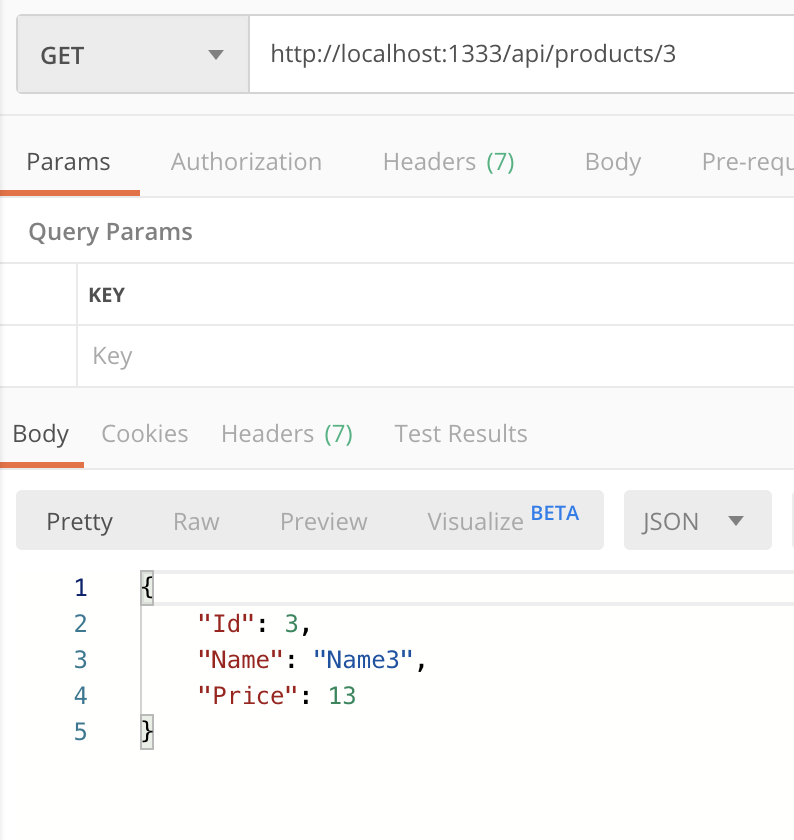
Now, we run the application and, using Postman, we can check everything works fine: