In this post, we will see some query examples to run in a MongoDB database.
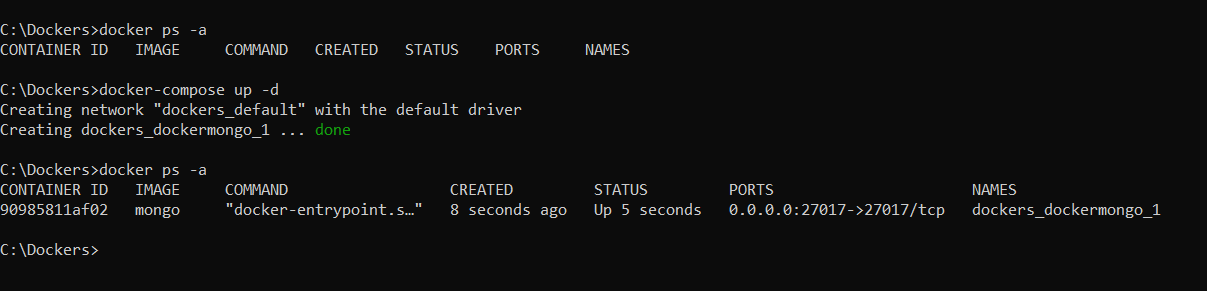
We start writing this Docker-compose file to create a docker container with an instance of MongoDB:
[DOCKER-COMPOSE.YML]
version: '3'
services:
# MongoDB container definition
dockermongo:
# name docker image
image: mongo
# username and password Admin definition
environment:
- MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=admindb
- MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=pass123
# volume definition
volumes:
- dbmongo:/data/db
ports:
- 27017:27017
volumes:
dbmongo:
driver: local
Now, we execute the docker-composer file and then, we will use NoSQLBooster to run queries in the database:
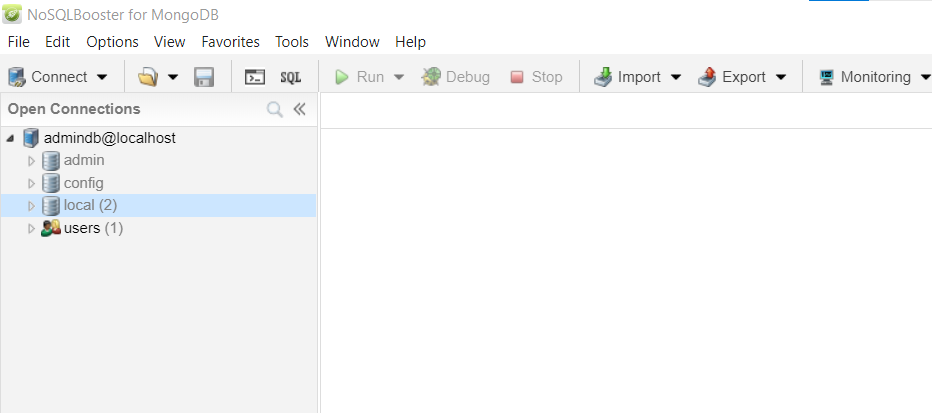
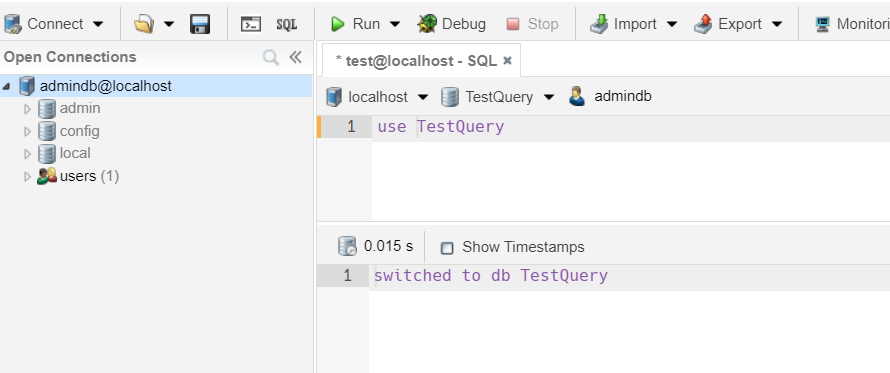
Now, we create a database called TestQuery:
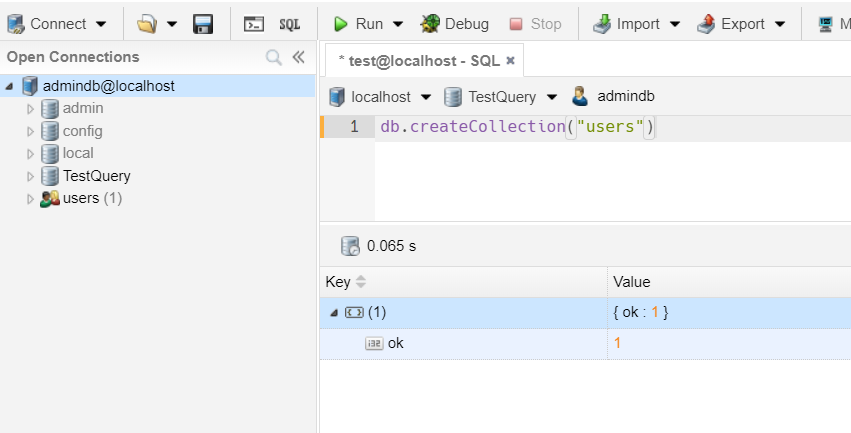
Then, we create a collection called users:
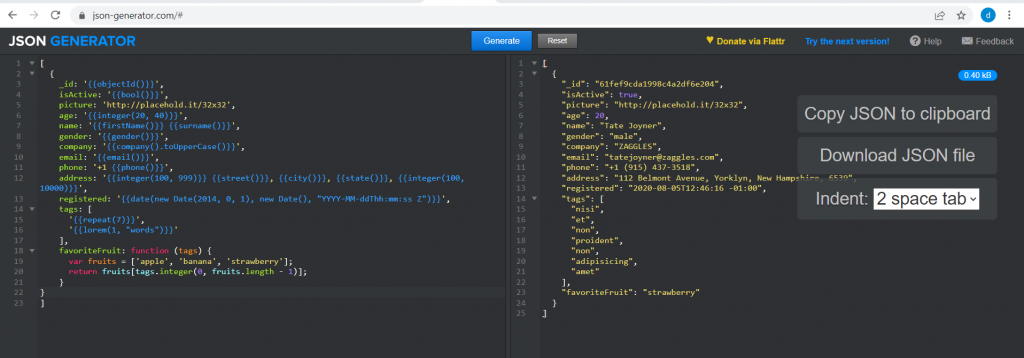
Finally, we will use the service https://json-generator.com/ to generate five random documents, based on this template, to insert in the Users collection:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | { _id: '{{objectId()}}', isActive: '{{bool()}}', picture: 'http://placehold.it/32x32', age: '{{integer(20, 40)}}', name: '{{firstName()}} {{surname()}}', gender: '{{gender()}}', company: '{{company().toUpperCase()}}', email: '{{email()}}', phone: '+1 {{phone()}}', address: '{{integer(100, 999)}} {{street()}}, {{city()}}, {{state()}}, {{integer(100, 10000)}}', registered: '{{date(new Date(2014, 0, 1), new Date(), "YYYY-MM-ddThh:mm:ss Z")}}', tags: [ '{{repeat(7)}}', '{{lorem(1, "words")}}' ], favoriteFruit: function (tags) { var fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'strawberry']; return fruits[tags.integer(0, fruits.length - 1)]; }} |
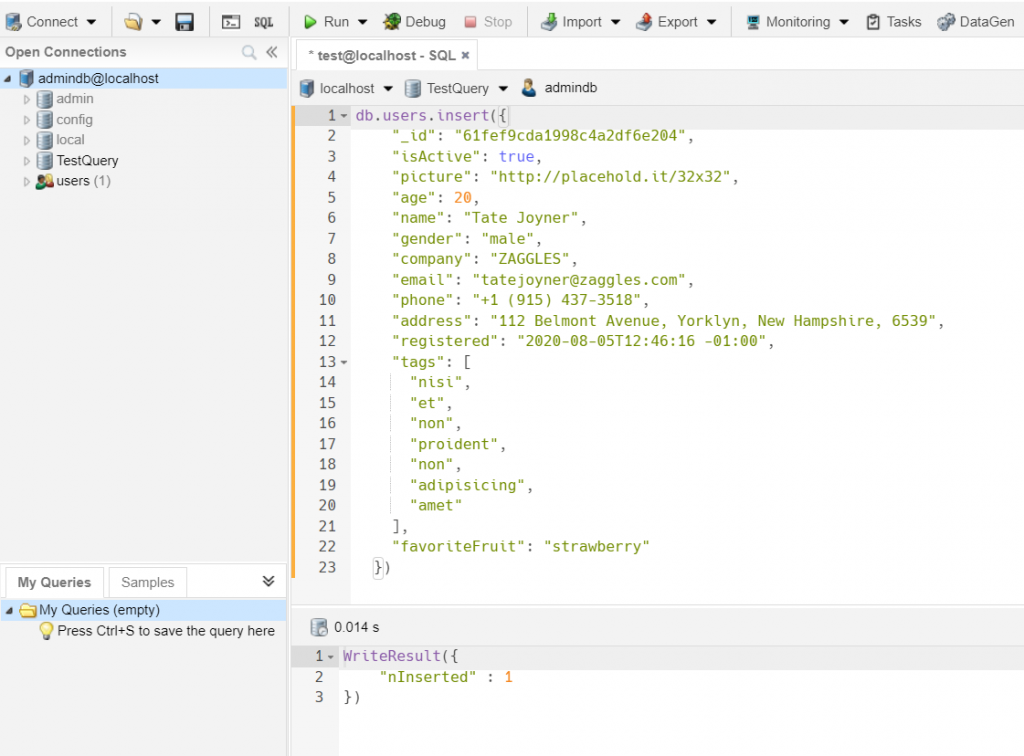
Now, after we feeded the database, we will run these queries for the Users collection:
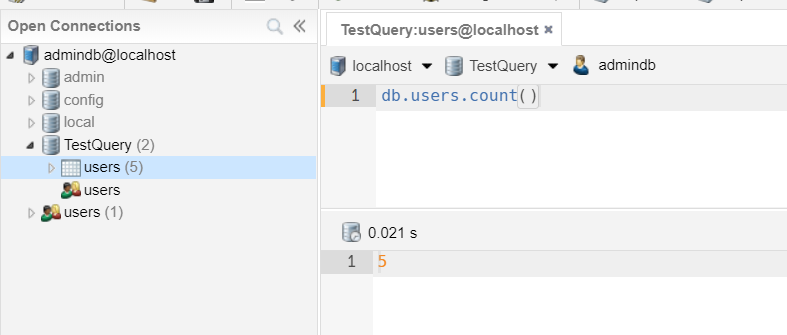
COUNT
1 | db.users.count() |
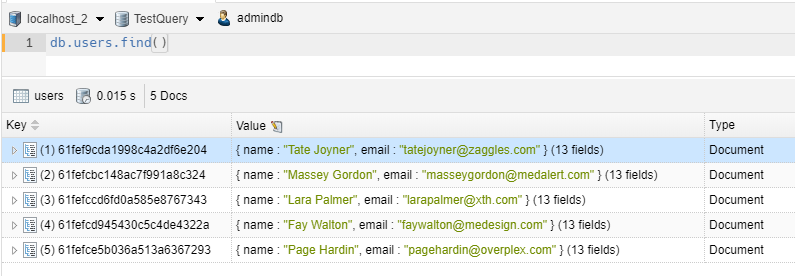
SELECT I
1 2 | // we take all itemsdb.users.find() |
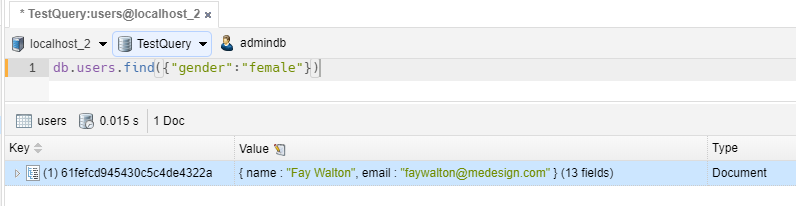
SELECT II
1 2 | // we take all items with gender equals to 'female'db.users.find({"gender":"female"}) |
1 2 | // we take all items with gender equals to 'male'db.users.find({"gender":"male"}) |
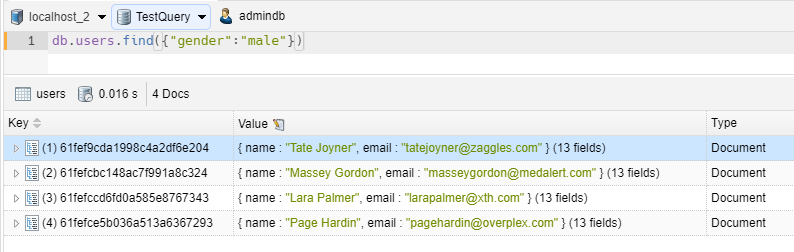
WHERE CLAUSE – GREATER THAN
1 2 | // we take all items with age greater than 33db.users.find({"age":{$gt:33}}) |
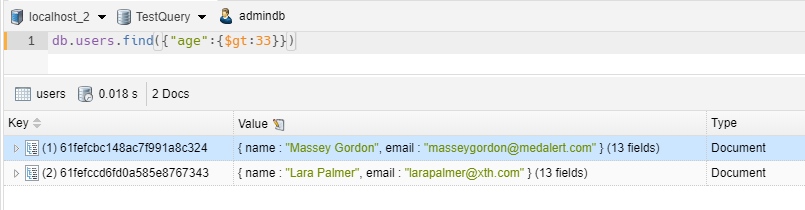
WHERE CLAUSE – GREATER THAN EQUALS
1 2 | // we take all items with age greater or equal at 33db.users.find({"age":{$gte:33}}) |
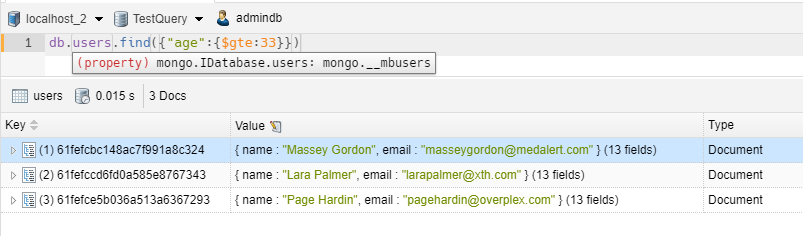
WHERE CLAUSE – LESS THAN
1 2 | // we take all items with age less than 33db.users.find({"age":{$lt:33}}) |
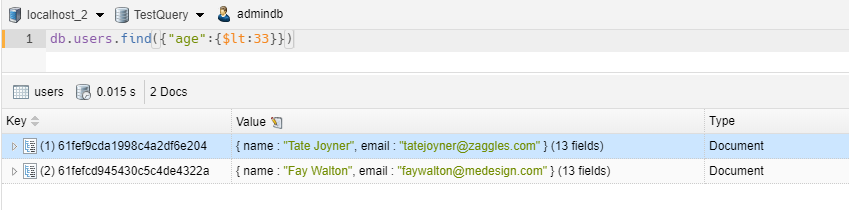
WHERE CLAUSE – LESS THAN EQUALS
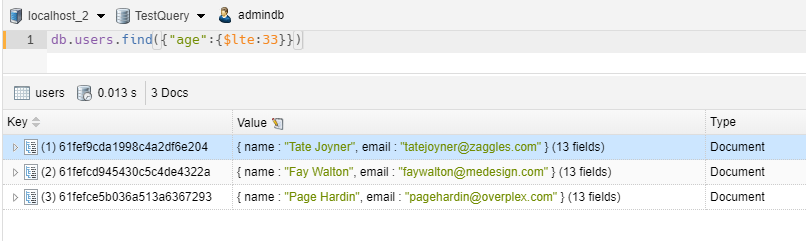
1 2 | // we take all items with age less and equal at 33db.users.find({"age":{$lte:33}}) |
WHERE CLAUSE – NOT EQUALS
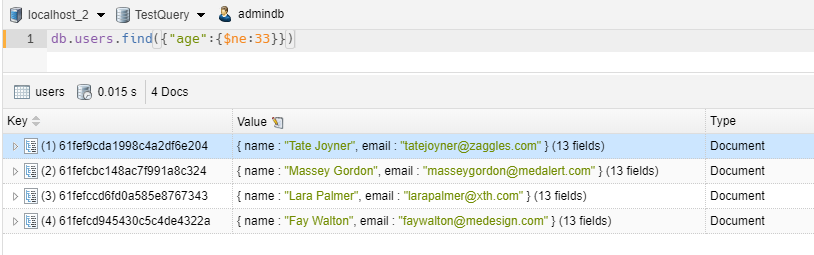
1 2 | // we take all items with age not equal 33db.users.find({"age":{$ne:33}}) |
AND
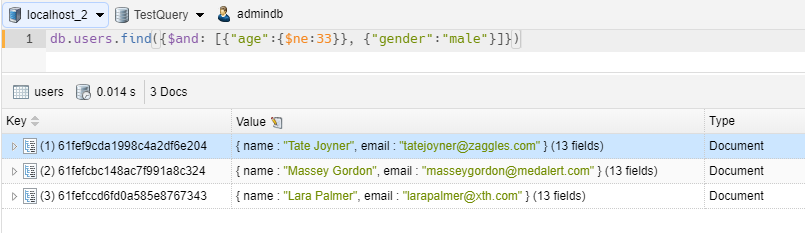
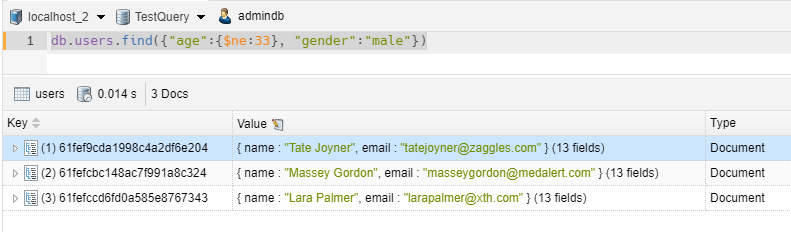
1 2 3 | // we take all items with age not equal 33 and gender = 'male'db.users.find({$and: [{"age":{$ne:33}}, {"gender":"male"}]})db.users.find({"age":{$ne:33}, "gender":"male"}) |
OR
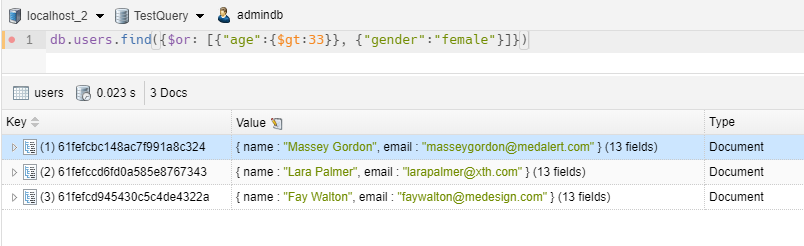
1 2 | // we take all items with age>33 or gender = 'female'db.users.find({$or: [{"age":{$gt:33}}, {"gender":"female"}]}) |
SELECT WITH SPECIFIC FIELDS
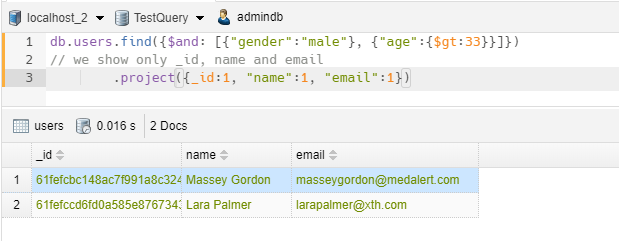
1 2 3 4 | // we take all items with gender = 'male' and age>33db.users.find({$and: [{"gender":"male"}, {"age":{$gt:33}}]})// we show only _id, name and email .project({_id:1, "name":1, "email":1}) |
LIMIT
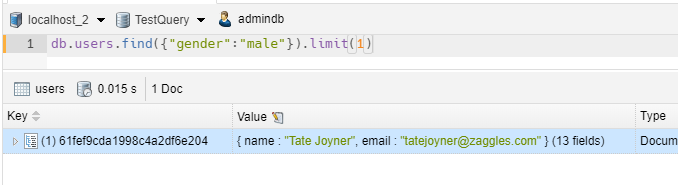
1 2 | // we show only 1 itemdb.users.find({"gender":"male"}).limit(1) |
SORT
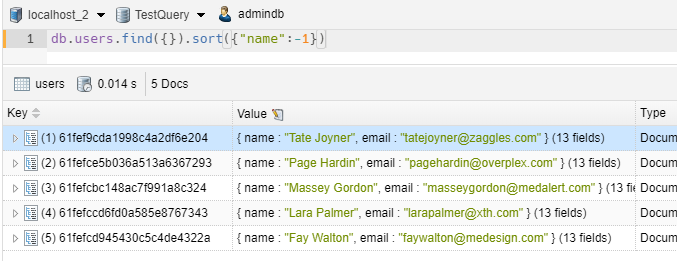
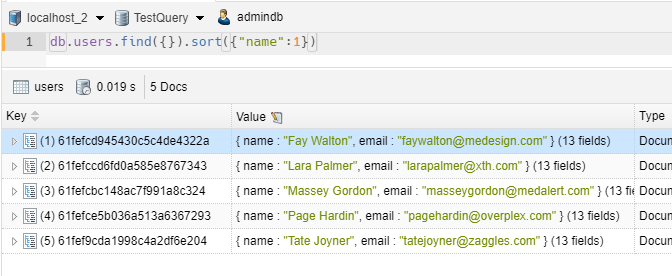
1 2 | // we sort by name in ascending orderdb.users.find({}).sort({"name":1}) |
1 2 | // we sort by name in descending orderdb.users.find({}).sort({"name":-1}) |