In this post, we will see the differences between WhenAll and WaitAll in the Asynchronous Programming.
We start creating a Console Application called TestAysncAwait where, we will add two classes called ClassWaitAllTest and ClassWhenAllTest:
[CLASSWAITALLTEST.COM]
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TestAsyncAwait
{
public class ClassWaitAllTest
{
public void RunTest()
{
Stopwatch checkTime = new Stopwatch();
checkTime.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Start method");
var result1 = Func1();
var result2 = Func2();
var result3 = Func3();
Task.WaitAll(result1, result2, result3);
checkTime.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"End method in {checkTime.Elapsed.TotalSeconds} seconds");
Console.WriteLine(result1.Result);
Console.WriteLine(result2.Result);
Console.WriteLine(result3.Result);
}
private async Task<int> Func1()
{
await Task.Delay(4000);
return 1;
}
private async Task<int> Func2()
{
await Task.Delay(2000);
return 2;
}
private async Task<int> Func3()
{
await Task.Delay(1000);
return 3;
}
}
}
[CLASSWHENALLTEST.COM]
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TestAsyncAwait
{
public class ClassWhenAllTest
{
public async Task RunTest()
{
Stopwatch checkTime = new Stopwatch();
checkTime.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Start method");
List<Task> lstTasks = new List<Task>();
lstTasks.Add(Func1());
lstTasks.Add(Func2());
lstTasks.Add(Func3());
await Task.WhenAll(lstTasks);
checkTime.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"End method in {checkTime.Elapsed.TotalSeconds}");
foreach(var item in lstTasks)
{
Console.WriteLine(((Task<int>)item).Result);
}
}
private async Task<int> Func1()
{
await Task.Delay(4000);
return 1;
}
private async Task<int> Func2()
{
await Task.Delay(2000);
return 2;
}
private async Task<int> Func3()
{
await Task.Delay(1000);
return 3;
}
}
}
Then, we modify the Program.cs file in order to run and testing ClassWaitAllTest:
[PROGRAMM.CS]
using System;
namespace TestAsyncAwait
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Testing WaiAll");
ClassWaitAllTest objWaitAll = new ClassWaitAllTest();
objWaitAll.RunTest();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
We have done and now, if we run the application, this will be the result:
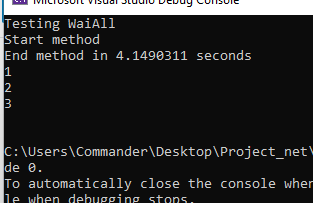
Finally, we modify the Program file again, in order to run and testing ClassWhenAllTest:
[PROGRAM.CS]
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TestAsyncAwait
{
internal class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Testing WhenAll");
ClassWhenAllTest objWhenAll = new ClassWhenAllTest();
await objWhenAll.RunTest();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
We have done and now, if we run the application, this will be the result:
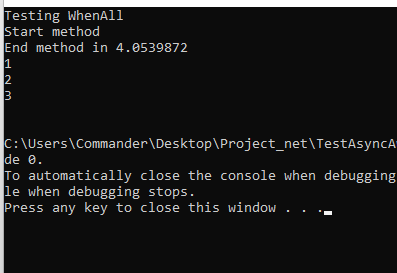
CONCLUSIONS
We can see that the results are the same: same time elapsed and same result.
The big difference between them is that WaitAll return a Void (it blocks the current thread) instead,
WhenAll, return a Task (we can decide to block or not the current thread).