Python – Streamlit (Part I)
Python – Streamlit (Part II)
In this last post on Streamlit, we will see how to manage a form Data, how to manage Buttons and Events and finally we will see how to manage the Session State.
FORM
Forms in Streamlit allow us to group multiple input widgets and submit them together, making it easier to manage related data.
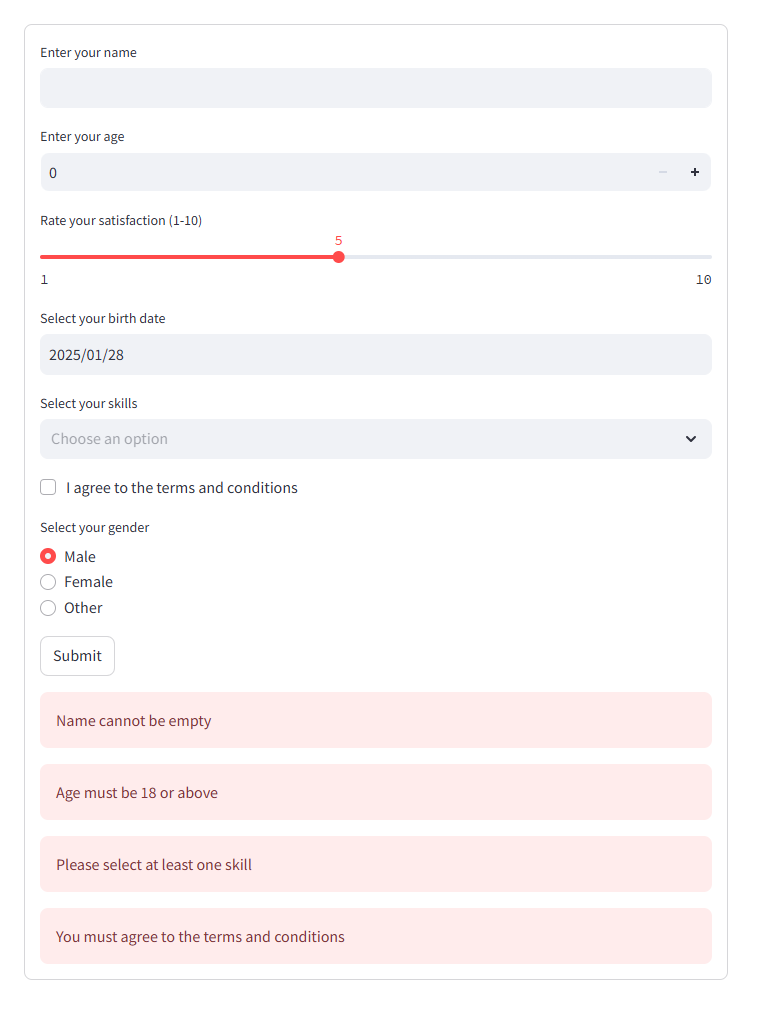
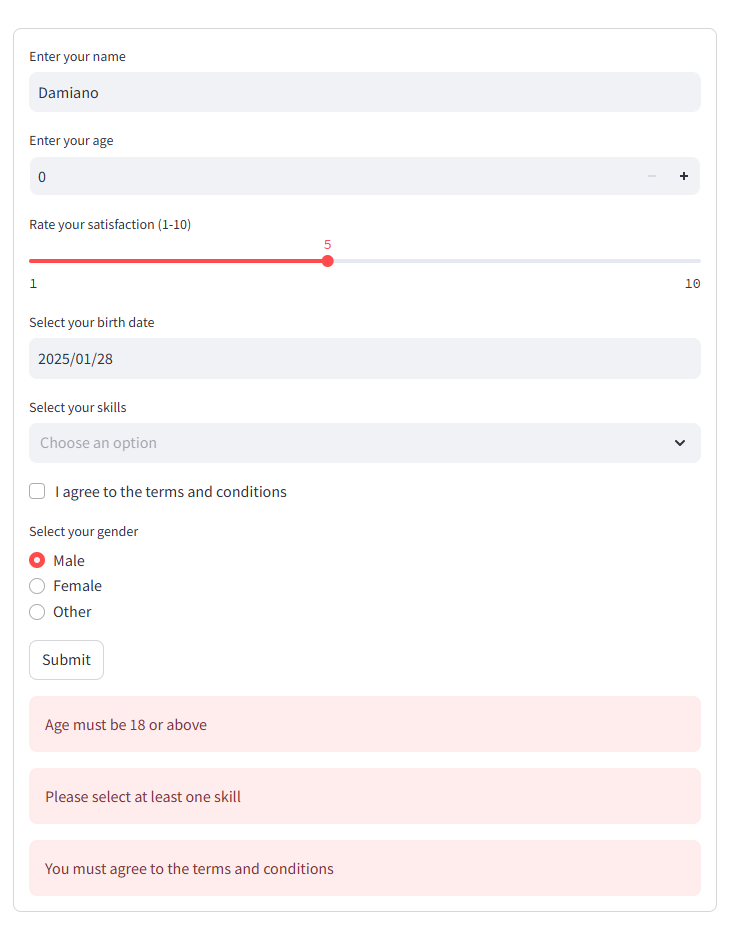
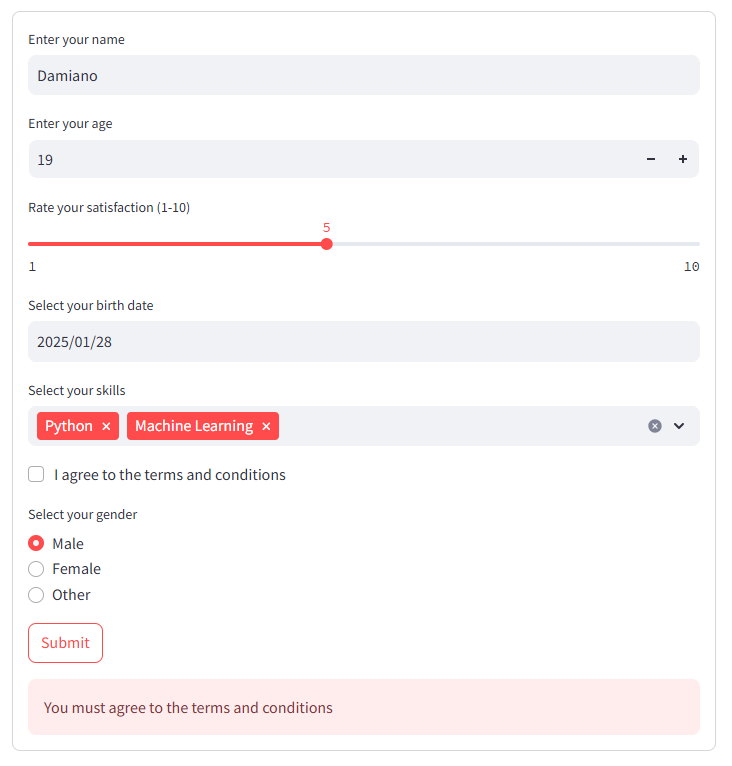
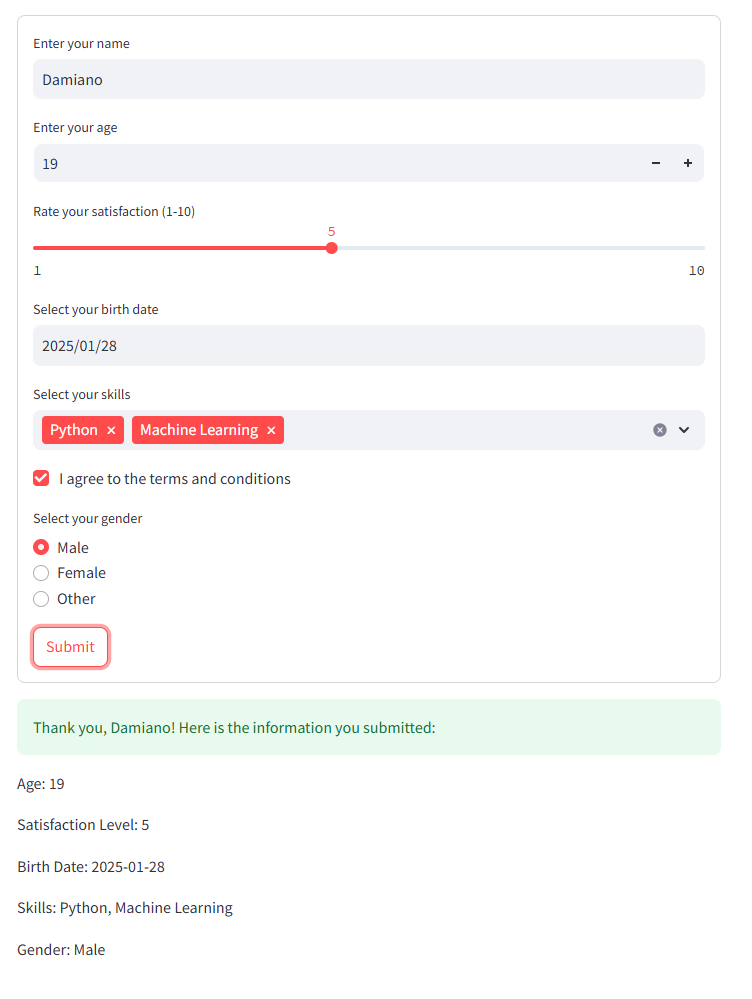
Let’s create a detailed form that incorporates various Streamlit widgets like sliders, date pickers, multi-selects, checkboxes, and radio buttons, along with validation checks:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 | import streamlit as st# Create a formwith st.form(key='detailed_form'): # Text input name = st.text_input("Enter your name") # Check if name is empty if name.strip() == "": st.error("Name cannot be empty") # Number input age = st.number_input("Enter your age", min_value=0, max_value=120, step=1) # Validate age if age < 18: st.warning("Age must be 18 or above") # Slider input satisfaction = st.slider("Rate your satisfaction (1-10)", min_value=1, max_value=10, value=5) # Date input birth_date = st.date_input("Select your birth date") # Validate date from datetime import date if birth_date > date.today(): st.error("Birth date cannot be in the future") # Multi-select input skills = st.multiselect("Select your skills", ["Python", "R", "SQL", "Machine Learning", "Data Visualization"]) # Ensure at least one skill is selected if not skills: st.warning("Please select at least one skill") # Checkbox input agree = st.checkbox("I agree to the terms and conditions") # Radio button input gender = st.radio("Select your gender", ["Male", "Female", "Other"]) # Submit button submitted = st.form_submit_button("Submit")# Handle form submissionif submitted: if agree: st.success(f"Thank you, {name}! Here is the information you submitted:") st.write(f"Age: {age}") st.write(f"Satisfaction Level: {satisfaction}") st.write(f"Birth Date: {birth_date}") st.write(f"Skills: {', '.join(skills)}") st.write(f"Gender: {gender}") else: st.error("You must agree to the terms and conditions to submit the form.") |
BUTTON AND EVENTS
Buttons are a core interactive component in Streamlit, and they can trigger specific actions or events:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | import streamlit as st # Initialize session state for dynamic messageif "dynamic_message" not in st.session_state: st.session_state.dynamic_message = "" # Define button actionsdef set_message(text): st.session_state.dynamic_message = text # Buttonsst.button("Say Hello", on_click=set_message, args=("Hello!",))st.button("Say Goodbye", on_click=set_message, args=("Goodbye!",)) # Display dynamic messagest.write(st.session_state.dynamic_message) |



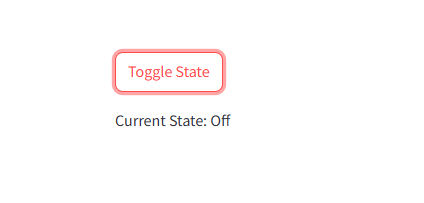
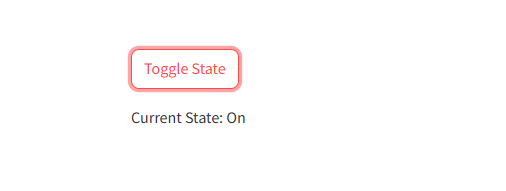
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | import streamlit as st# Toggle a boolean stateif "toggle" not in st.session_state: st.session_state.toggle = Falseif st.button("Toggle State"): st.session_state.toggle = not st.session_state.togglest.write(f"Current State: {'On' if st.session_state.toggle else 'Off'}") |
SESSION STATE
Session state allows us to store and manipulate data across user interactions and app reruns:
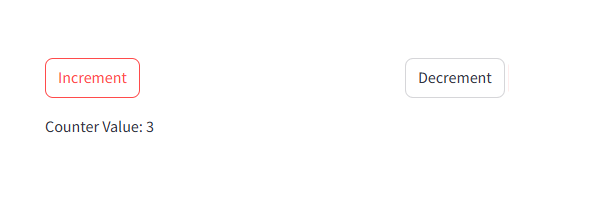
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | import streamlit as st# Initialize session state for counterif "counter" not in st.session_state: st.session_state.counter = 0# Increment and Decrement Buttonscol1, col2 = st.columns(2)with col1: if st.button("Increment"): st.session_state.counter += 1with col2: if st.button("Decrement"): st.session_state.counter -= 1st.write(f"Counter Value: {st.session_state.counter}") |


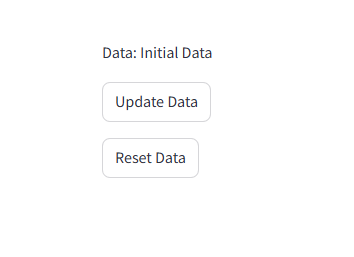
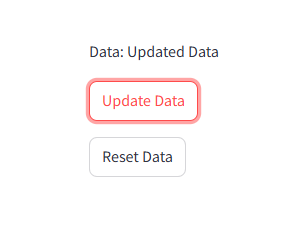
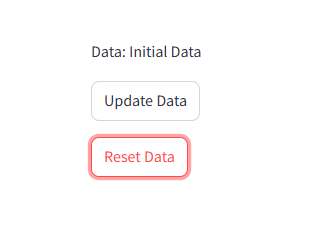
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | import streamlit as st# Initialize session state variablesif "resettable_data" not in st.session_state: st.session_state.resettable_data = "Initial Data"# Function to update the state and force a rerundef update_data(): st.session_state.resettable_data = "Updated Data"def reset_data(): st.session_state.resettable_data = "Initial Data"# Display current statest.write(f"Data: {st.session_state.resettable_data}")# Buttons with actionsst.button("Update Data", on_click=update_data)st.button("Reset Data", on_click=reset_data) |